How to make mining more sustainable
As mining ramps up to supply minerals for renewable power projects and electrification, how can we protect communities and the environment?
The growing demand for renewable energy technology and electrification presents a paradox. While these technologies are critical for achieving net-zero targets, their production relies heavily on mining for critical minerals — an industry that can have harmful environmental and social impacts.
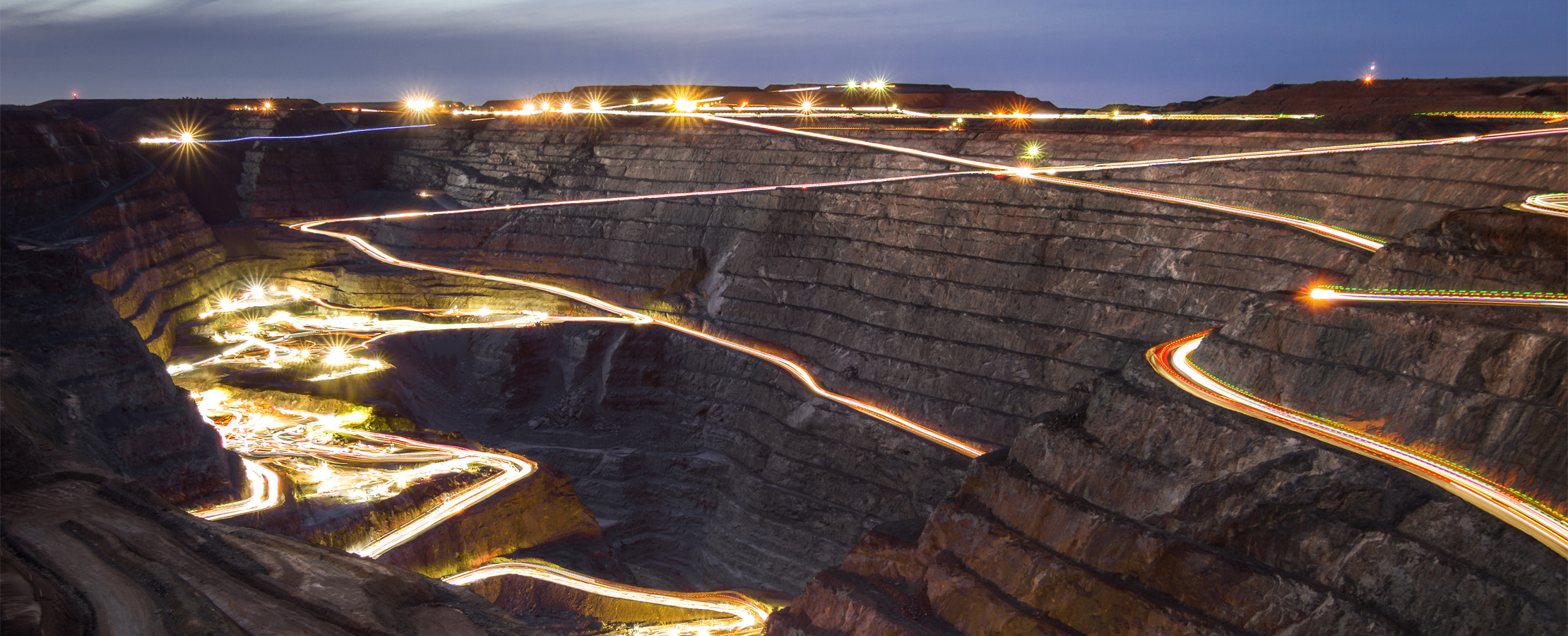
Mining operations are widely recognized for their significant resource demands and substantial environmental footprint. By its very nature, mining disrupts the natural environment. Poorly regulated, large-scale operations can lead to habitat destruction, pollution, soil degradation, resource depletion, toxic waste, and community disruption.
How can we secure the raw materials to build renewable technology without imposing an unacceptable toll on the environment that the technologies aim to preserve?
Mining is essential to the energy transition
The ability to build renewable technology hinges on the availability of a few crucial metals.
Lithium, for example, is a vital component of lithium-ion batteries. Cobalt is an essential part of lithium-ion battery cathodes. Nickel is increasingly important in batteries used in electric vehicles. Copper, one of the most widely extracted metals, is used for wind power, wiring, and motors. Rare earth metals (a group of 17 elements with unique properties) are crucial in technologies like lighting, catalytic converters, magnets for wind turbines, EVs, and hard drives.
The World Bank estimates the production of minerals like lithium and cobalt could increase by nearly 500% by 2050, and that 3 billion tons of minerals and metals will be needed to build the infrastructure to meet global climate targets.
The high cost of metal extraction
Even at current demand levels, mining has a significant environmental impact, and workers often face dangerous working conditions.
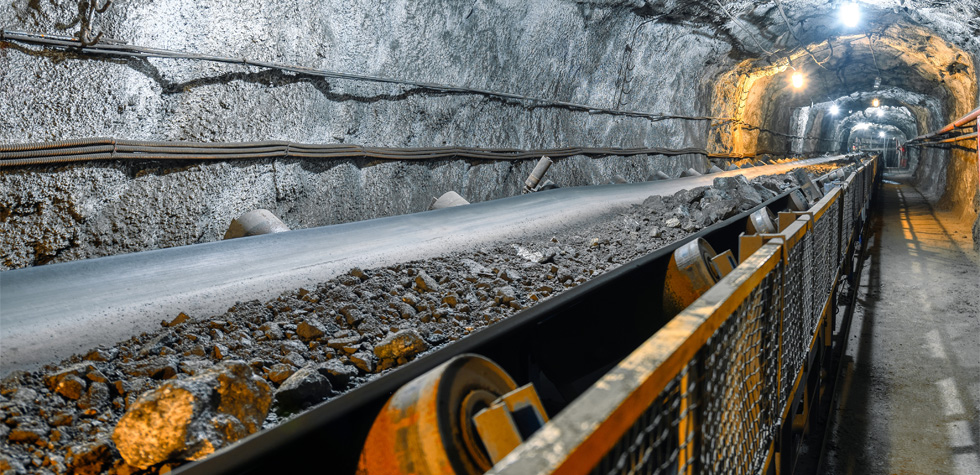

Disasters have also called attention to the impact mining can have on the natural environment, such as the 2015 collapse of a Brazilian mine. The collapse released a flood of toxic mud, killing 20 people and millions of freshwater fish, degrading surrounding indigenous land and polluting the sea and nesting areas for vulnerable turtles.
Given the harmful impact of unregulated metal extraction, the growth of renewable energy will also require a major push to make mining more sustainable.
The transition to sustainable mining
Recognizing a need for change, the mining industry is actively working towards a greener, more ethical framework. The importance of environmentally sound mining has been recognized at the highest levels of government, including in the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro and the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development. The Intergovernmental Forum of Mining, Minerals, Metals and Sustainable Development is dedicated to driving sustainability in mining, supporting 79 member states.
The mining industry has identified several ways to build sustainability into mining.
- Implementing sustainable practices: Tailing reuses extracted residual metals from previous mining projects, minimizing waste and impact. Additionally, ensuring waste is managed safely and efficiently can prevent disasters.
- Land rehabilitation involves reversing the impact of mining after a project is complete, through reforestation and waste management. Working more closely with surrounding communities can minimize the effect of mining on a community, or even turn it into a positive.
- Shifting from coal power to renewable energy sources: Taking advantage of the very technology it’s producing, mines that shift from coal to renewable energy sources to power their operations can cut down on their emissions. Chile, Mauritius and South Africa are already leading in providing renewable power to mining sites. Globally, 1 GW of renewables is already operational at mining sites, with another 1 GW in development, signaling a promising shift towards cleaner energy sources.
- Carbon capture: Advanced carbon capture and storage techniques could help the mining industry to decarbonize. Some experts have suggested that emerging technology may even be able to help miners transition to carbon negative. Through tweaking or accelerating natural processes like mineralization, experts have identified ways to trap or store carbon in the mining process, neutralizing the industry’s carbon footprint.
- Technological innovations: Technology is significantly improving sustainability in mining. It improves the transportation of minerals and metals, can reduce waste and enhances emergency response procedures. Technological innovation also directly contributes to environmental protection through waste management, water usage, and energy usage. Moreover, techniques like precision drilling mean mining activities are more accurately targeted.
As the demand for metals and minerals grows, their method of extraction will play an equally important role in conservation. Supporting sustainability in mining through policymaking, improved practices and innovation will be a key aspect of a successful energy transition.